Enzymes and cellular regulation pogil answers delve into the fascinating realm of biochemistry, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding the structure, function, and regulation of enzymes, the molecular workhorses that drive cellular processes. This discourse will illuminate the intricate mechanisms that govern enzyme activity, empowering readers with a profound grasp of cellular regulation.
Enzymes, the catalysts of life, facilitate biochemical reactions within cells, enabling the smooth functioning of metabolic pathways and cellular homeostasis. This exploration will unveil the diverse types of enzymes, their specific roles, and the regulatory mechanisms that ensure their precise control.
Furthermore, the practical applications of enzymes in biotechnology and industry will be examined, showcasing their indispensable contributions to modern science and technology.
Enzyme Basics: Enzymes And Cellular Regulation Pogil Answers
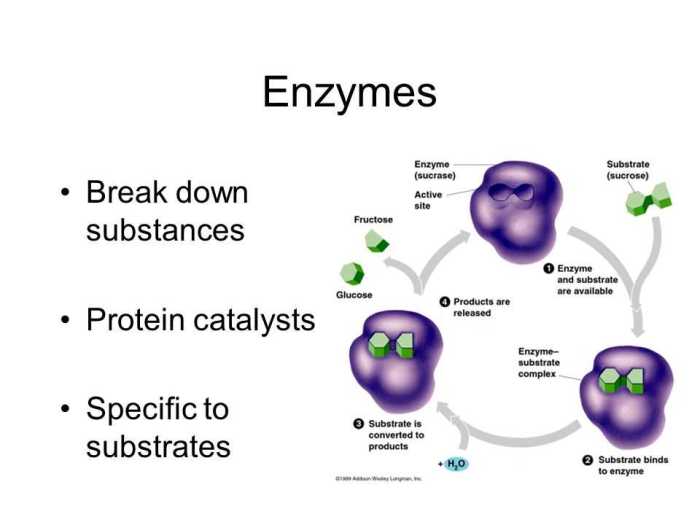
Enzymes are biological molecules that catalyze chemical reactions within living organisms. They are highly specific, each enzyme catalyzing a specific chemical reaction. Enzymes are composed of amino acids and are produced by cells.Enzymes have a complex structure, consisting of an active site, a substrate-binding site, and a cofactor-binding site.
The active site is where the substrate binds to the enzyme, and the substrate-binding site is where the enzyme binds to the substrate. The cofactor-binding site is where the cofactor binds to the enzyme.There are many different types of enzymes, each with a specific function.
Some of the most common enzymes include:
- Digestive enzymes, which break down food into smaller molecules
- Metabolic enzymes, which catalyze the chemical reactions that occur in cells
- Regulatory enzymes, which control the activity of other enzymes
Enzyme Regulation
Enzymes can be regulated in a number of ways, including:
- Feedback inhibition, which occurs when the end product of a reaction inhibits the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction
- Allosteric regulation, which occurs when a molecule binds to the enzyme and changes its activity
- Covalent modification, which occurs when a chemical group is added to or removed from the enzyme
Enzyme regulation is important for controlling the rate of chemical reactions in cells. For example, feedback inhibition helps to prevent the accumulation of excess end products, and allosteric regulation helps to coordinate the activity of different enzymes in a metabolic pathway.
Enzyme Kinetics

Enzyme kinetics is the study of the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is determined by a number of factors, including:
- The concentration of the enzyme
- The concentration of the substrate
- The temperature
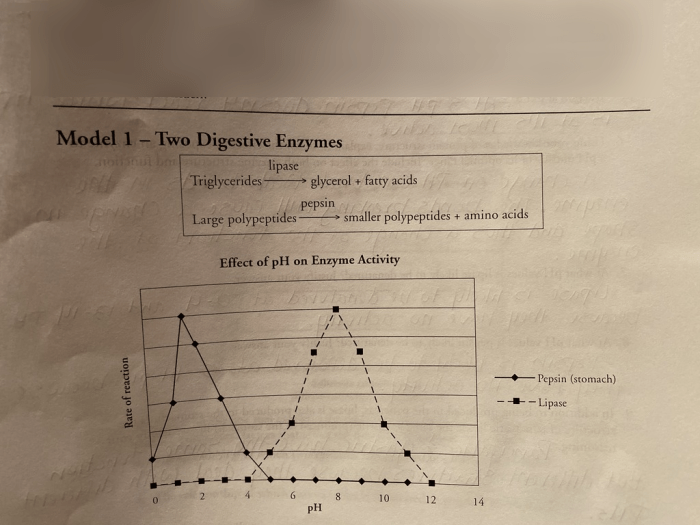
- The pH
Enzyme kinetics can be used to study the mechanism of enzyme action and to determine the kinetic parameters of an enzyme. The kinetic parameters of an enzyme are the values of the Michaelis constant (Km) and the maximum velocity (Vmax).
The Km is the concentration of substrate at which the enzyme is half-saturated, and the Vmax is the maximum rate of the reaction.
Enzyme Applications
Enzymes have a wide range of applications in biotechnology and industry. Some of the most common applications of enzymes include:
- Food processing, where enzymes are used to break down food into smaller molecules, making it easier to digest
- Pharmaceuticals, where enzymes are used to produce antibiotics, hormones, and other drugs
- Textile industry, where enzymes are used to break down starch and other materials
- Paper industry, where enzymes are used to bleach paper
- Leather industry, where enzymes are used to remove hair from hides
Questions Often Asked
What is the primary function of enzymes?
Enzymes act as catalysts, facilitating and accelerating biochemical reactions within cells.
How are enzymes regulated within cells?
Enzyme regulation involves various mechanisms, including feedback inhibition, allosteric regulation, and covalent modifications.
What is the significance of enzyme kinetics in understanding enzyme function?
Enzyme kinetics provides insights into the factors affecting enzyme activity, such as substrate concentration, temperature, and pH, enabling the optimization of enzymatic reactions.