Unit 1 The Living World Ecosystems Answer Key unveils the intricate tapestry of Earth’s ecosystems, providing a comprehensive guide to their fundamental concepts, energy flow, nutrient cycling, ecological interactions, and human impacts. Delve into the fascinating world of ecosystems and uncover their vital role in sustaining life on our planet.
This comprehensive resource offers a wealth of knowledge, empowering you to understand the interconnectedness of living organisms and their environments. Explore the flow of energy through food chains and webs, unravel the processes of nutrient cycles, and witness the dynamic interactions between species that shape ecosystems.
1. Ecosystem Concepts
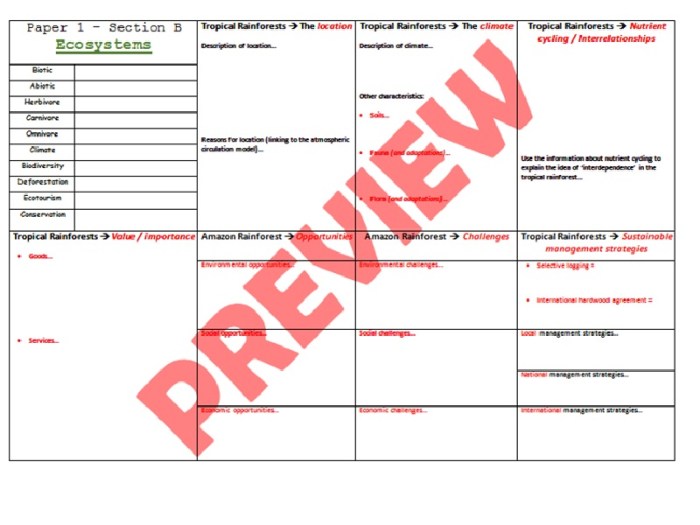
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and soil), interacting as a system. Ecosystems are important because they provide the basic necessities for life, such as food, water, and shelter.
They also play a role in regulating the Earth’s climate and maintaining biodiversity.
There are many different types of ecosystems, each with its own unique characteristics. Some of the most common types of ecosystems include forests, grasslands, deserts, and aquatic ecosystems.
2. Energy Flow in Ecosystems
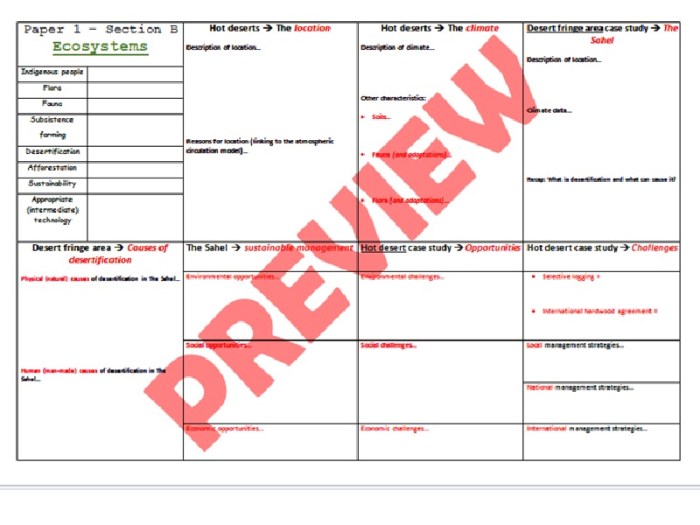
Energy flows through ecosystems in a one-way direction, from producers to consumers to decomposers. Producers are organisms that can make their own food from inorganic matter, such as plants and algae. Consumers are organisms that cannot make their own food and must eat other organisms to obtain energy, such as animals and fungi.
Decomposers are organisms that break down dead organisms and return their nutrients to the ecosystem, such as bacteria and fungi.
The amount of energy that flows through an ecosystem is determined by the amount of sunlight that is available. Sunlight is the primary source of energy for all life on Earth, and it is used by plants to produce food through photosynthesis.
The food that plants produce is then eaten by consumers, and the energy that is stored in the food is passed up the food chain.
3. Nutrient Cycling in Ecosystems: Unit 1 The Living World Ecosystems Answer Key

Nutrient cycles are the pathways by which nutrients move through ecosystems. Nutrients are essential for life, and they are used by organisms to build and repair tissues, produce energy, and regulate body processes.
The three main nutrient cycles are the water cycle, the carbon cycle, and the nitrogen cycle. The water cycle is the process by which water moves through the Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, and land. The carbon cycle is the process by which carbon moves through the Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, and land.
The nitrogen cycle is the process by which nitrogen moves through the Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, and land.
4. Ecological Interactions
Ecological interactions are the interactions that occur between organisms in an ecosystem. These interactions can be positive, negative, or neutral.
Some of the most common types of ecological interactions include competition, predation, and symbiosis. Competition occurs when two or more organisms compete for the same resources, such as food or water. Predation occurs when one organism eats another organism. Symbiosis is a close relationship between two or more organisms, in which both organisms benefit from the relationship.
5. Human Impact on Ecosystems
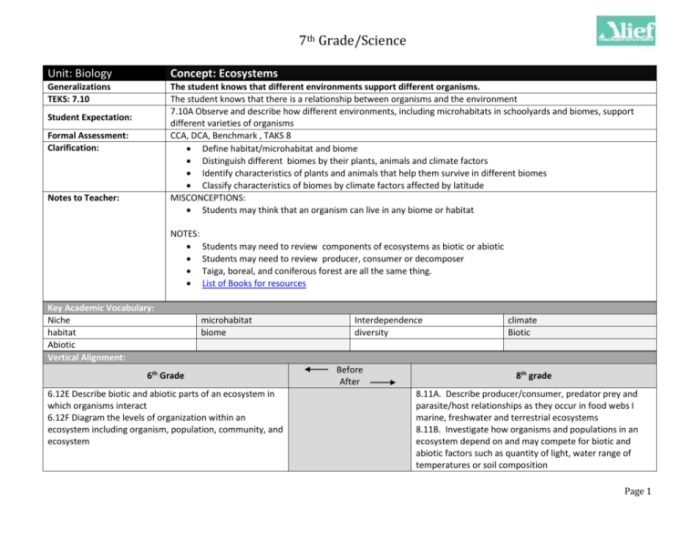
Humans have a significant impact on ecosystems. We can alter the structure and function of ecosystems through our activities, such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change.
Deforestation is the clearing of forests for other uses, such as agriculture or development. Deforestation can lead to a loss of biodiversity, soil erosion, and climate change.
Pollution is the introduction of harmful substances into the environment. Pollution can come from a variety of sources, such as factories, cars, and agriculture. Pollution can damage ecosystems and harm human health.
Climate change is the long-term alteration of temperature and typical weather patterns in a place. Climate change is caused by the release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, which trap heat and cause the planet to warm.
Query Resolution
What is the significance of ecosystems?
Ecosystems are essential for maintaining the balance of life on Earth. They provide vital resources such as food, water, and shelter, regulate the climate, and support biodiversity.
How does energy flow through ecosystems?
Energy enters ecosystems through producers (plants) and is transferred through food chains and webs as consumers (animals) feed on each other.
What is the role of nutrient cycles in ecosystems?
Nutrient cycles, such as the water cycle, carbon cycle, and nitrogen cycle, ensure the availability of essential nutrients for living organisms.
How can human activities impact ecosystems?
Human activities such as habitat loss, pollution, and climate change can disrupt ecosystem structure and function, leading to biodiversity loss and environmental degradation.